High priority jobs¶
This example demonstrates how high-priority tokens can be used within Artemis. It enables jobs to skip to the front of the queue, which may be useful when trying to perform real-time computations on the system that require submission of jobs based on the results from previous jobs. This capability can be assigned to users by your system administrator for a limited period of time, but should only be used where necessary for a computation.
In this notebook, it is assumed you have the high-priority capability, but if not then it should be possible to follow along without this.
Token creation¶
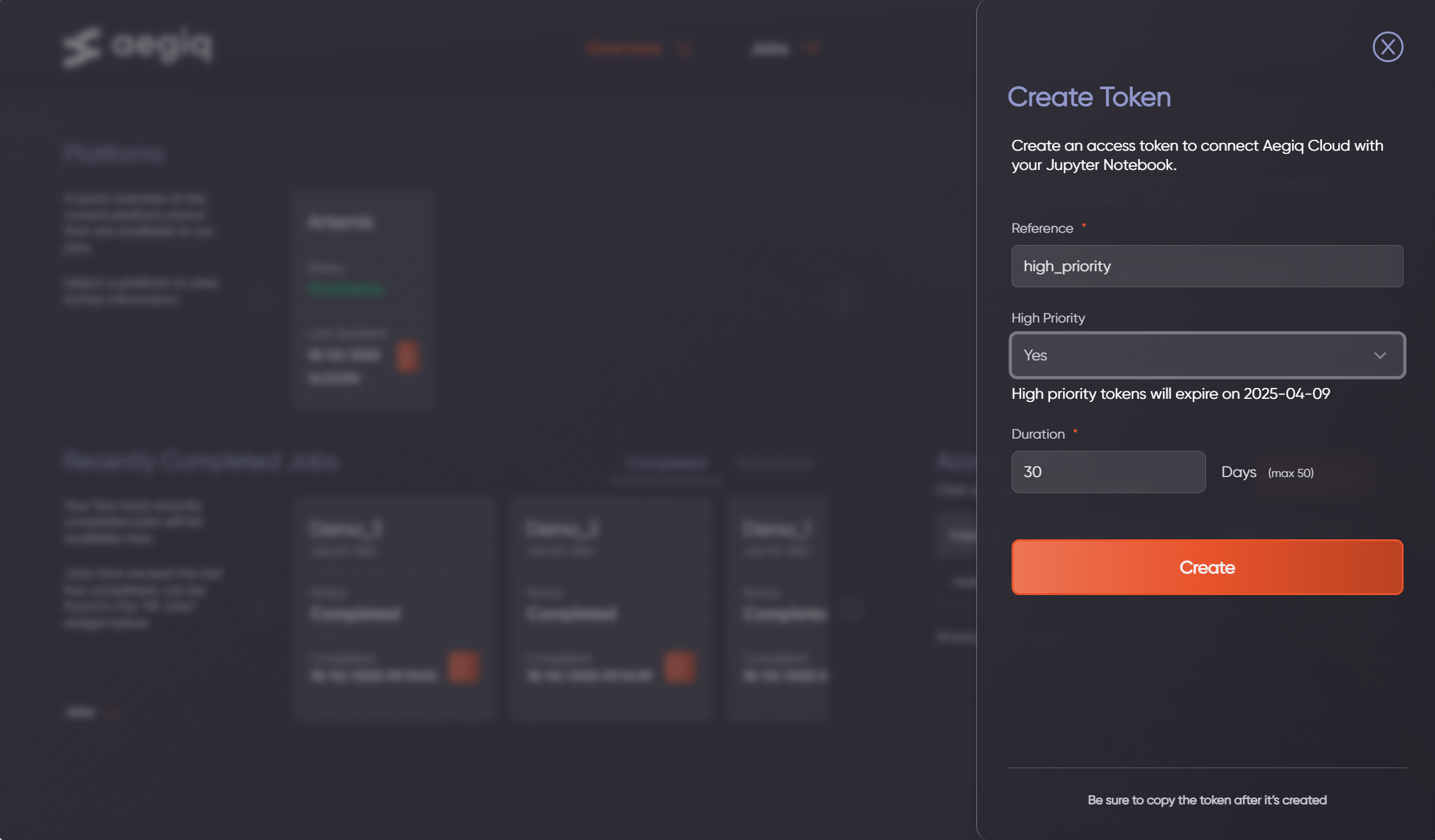
To submit high-priority jobs to the scheduler, an access token with the high-priority attribute needs to be created. This token can be used at the same time as other normal-priority tokens to switch between scheduling mode as required.
To create a high-priority token, users must be assigned this capability by their administrator. Once done, when creating a new token the high-priority field can be set to yes, which enables the capability for a user.

Job submission¶
Once created, this token can then be used the same way as any other token would be, using the token management system to set, save & load as required.
[1]:
import lightworks as lw
from lightworks import remote
remote.token.set("HIGH_PRIORITY_TOKEN")
A basic sampling job can then be created and submitted. If there are other jobs in the queue when the job is submitted then these will be bypassed.
[3]:
qpu = remote.QPU("Artemis")
sampler = lw.Sampler(
circuit=lw.Unitary(lw.random_unitary(6)),
input_state=lw.State([1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0]),
n_samples=1000,
)
job = qpu.run(sampler)
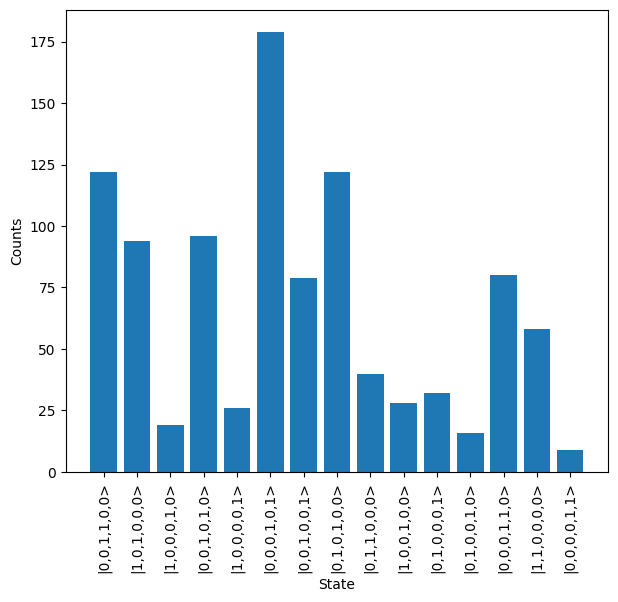
Once complete, results can be retrieved from the system & plotted.
[4]:
job.wait_until_complete()
results = job.get_result()
results.plot()